Series C Paper Size Chart
| C Paper Size | Dimensions (inches) | Dimensions (mm) | Area (mm²) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
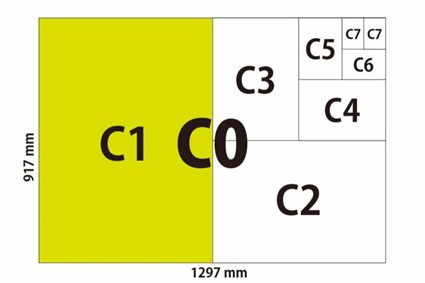
| C0 Size | 36.1 × 51 | 917 × 1297 | 1189349 | ||||||
| C1 Size | 25.5 × 36.1 | 648 × 917 | 594216 | ||||||
| C2 Size | 18 × 25.5 | 458 × 648 | 296784 | ||||||
| C3 Size | 12.8 × 18 | 324 × 458 | 148392 | ||||||
| C4 Size | 9 × 12.8 | 229 × 324 | 74196 | ||||||
| C5 Size | 6.4 × 9 | 162 × 229 | 37098 | ||||||
| C6 Size | 4.5 × 6.4 | 114 × 162 | 18468 | ||||||
| C7 Size | 3.2 × 4.5 | 81 × 114 | 9234 | ||||||
| C8 Size | 2.2 × 3.2 | 57 × 81 | 4617 | ||||||
| C9 Size | 1.6 × 2.2 | 40 × 57 | 2280 | ||||||
| C10 Size | 1.1 × 1.6 | 28 × 40 | 1120 | ||||||
| Series C Paper Size Chart Maker : iSizeChart.com | |||||||||
About Series C Paper Size Chart
How are the C series paper sizes defined?
The C series paper sizes, standardized in ISO 269 (primarily for envelopes), are defined as the geometric mean between corresponding sizes in the A series and B series. This ensures envelopes perfectly fit A-series sheets while accounting for paper thickness and folding. Here’s the precise definition:
1. Core Principles:
The largest size, C0, is derived as the geometric mean of A0 and B0:
Width(C0) = √(Width(A0) × Width(B0))
Height(C0) = √(Height(A0) × Height(B0))
②. Constant Aspect Ratio:
All C sizes maintain the aspect ratio 1:√2 (≈1:1.4142), identical to A and B series.
③. Geometric Mean Relationship:
C𝑛 = Geometric Mean(A𝑛, B𝑛)
Width(C𝑛) = √(Width(A𝑛) × Width(B𝑛))
Height(C𝑛) = √(Height(A𝑛) × Height(B𝑛))
2. Deriving Dimensions:
Width(C0) = √(841 × 1000) ≈ √841,000 ≈ 917 mm
Height(C0) = √(1189 × 1414) ≈ √1,681,246 ≈ 1297 mm
C0 = 917 mm × 1297 mm
②. Smaller Sizes (via Halving):
Halve the longer side to generate subsequent sizes (same as A/B series):
C1: Halve C0 height → 917 × 648 mm
C2: Halve C1 width → 648 × 458 mm
(Exact dimensions use geometric mean then rounded to mm).
③. Practical Example (C4):
A4 = 210 × 297 mm, B4 = 250 × 353 mm
Width(C4) = √(210 × 250) = √52,500 ≈ 229 mm
Height(C4) = √(297 × 353) = √104,841 ≈ 324 mm
C4 = 229 mm × 324 mm
3. Key Purpose & Characteristics:
A flat sheet of size A𝑛 fits perfectly in C𝑛.
A sheet folded once (e.g., A3 folded to A4) fits in C(𝑛-1).
Example: C4 holds an unfolded A4 sheet. C5 holds A4 folded once (A5 size) or an unfolded A5 sheet.
②. Paper Thickness Allowance: The geometric mean provides ~3% extra space, accommodating paper thickness and folds without forcing or gaping.
③. Nesting Compatibility: C-series envelopes themselves fit neatly into larger B-series envelopes (e.g., C4 envelope fits inside B4 envelope).
④. Tolerances: Follows ISO 216 (typically ±1–1.5 mm).
4. Why the C Series Matters:
Efficient Design: Eliminates guesswork—each C𝑛 snugly fits A𝑛 with room for thickness.
Scalability: Maintains the √2 ratio, allowing consistent scaling between envelope sizes.
Note: The C series is occasionally used for postcards (C6) or notepads, but its core purpose remains envelopes. Like A/B series, it originated from Georg Lichtenberg’s 1786 principles and was formalized in ISO standards later.
The C series completes the ISO paper ecosystem: A for sheets, B for intermediate needs, C for encapsulation—all sharing the same mathematical harmony.