Paper Size Chart
About Paper Size Chart
How are different paper sizes defined?
Paper sizes are defined through standardized systems that vary by region and purpose. The most globally recognized systems are the ISO 216 standard (A/B/C series) and the ANSI/ARCH series (North America), alongside regional variations. Below is a clear breakdown:
1. ISO 216 Standard (International).
Key Series:
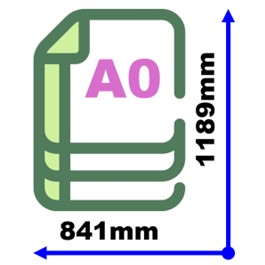
A Series (General printing). A0 = 1 m² area (841 × 1189 mm). Each smaller size (A1, A2, etc.) = half the longer side of the previous sheet. Example: A4 = 210 × 297 mm.
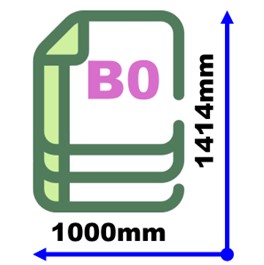
B Series (Intermediate sizes). B0 = 1-meter width (1000 × 1414 mm). B𝑛 = Geometric mean between A𝑛 and A(𝑛-1). Example: B4 = 250 × 353 mm (between A3 and A4).
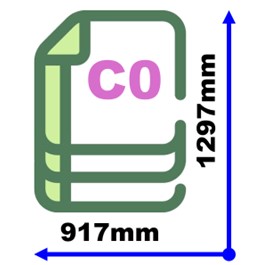
C Series (Envelopes). C𝑛 = Geometric mean between A𝑛 and B𝑛. Example: C4 envelope (229 × 324 mm) holds unfolded A4 paper.
Advantages:
Scalability (enlarge/reduce without distortion).
Nesting efficiency (two A4 sheets fit perfectly on A3).
2. ANSI/ARCH Series (North America).
① ANSI Series (General use):
Letter = 8.5 × 11 in (216 × 279 mm) – Most common in US offices.
Legal = 8.5 × 14 in (216 × 356 mm).
Tabloid/Ledger = 11 × 17 in (279 × 432 mm).
Larger sizes (ANSI A-E) created by doubling shorter sides:
ANSI A = Letter (8.5 × 11 in). ANSI B = Tabloid (11 × 17 in). ANSI C = 17 × 22 in, etc.
②. ARCH Series (Architectural drawings):
ARCH A = 9 × 12 in (229 × 305 mm).
Scales up to ARCH E6 = 36 × 48 in (914 × 1219 mm).
Limitations: No consistent aspect ratio (scaling requires cropping). Letter size differs from A4, causing compatibility issues.
3. Regional Standards.
Slightly different from ISO B.
Example: JIS B4 = 257 × 364 mm (vs. ISO B4 = 250 × 353 mm).
②. Chinese Standards:
Follows ISO A/B but includes unique sizes like "Kai" for books.
4. Specialty Sizes.
Untrimmed raw paper for printing.
SRA0 = 900 × 1280 mm (larger than A0 to allow for bleed).
②. Business Cards:
ISO 216: A8 (74 × 52 mm).
US Standard: 3.5 × 2 in (89 × 51 mm).
5. Why Standards Matter.
Design Efficiency: ISO’s √2 ratio enables seamless scaling.
Envelope Pairing: C series ensures precise fit for A series sheets.
Historical Roots: ISO based on Georg Lichtenberg’s 1786 principles; ANSI evolved from papermaking traditions.
Practical Tip: Always specify ISO A4 or US Letter when sharing documents internationally to avoid formatting issues. For printing, use SRA sizes to include bleed areas.
This system of paper sizing balances mathematical elegance (ISO) with historical practicality (ANSI), reflecting cultural and industrial priorities worldwide.